What can a hidden state see?
We can visualise the forward pass of a transformer by unrolling the input tokens on the x-axis and laying out the layers on the y-axis like so:
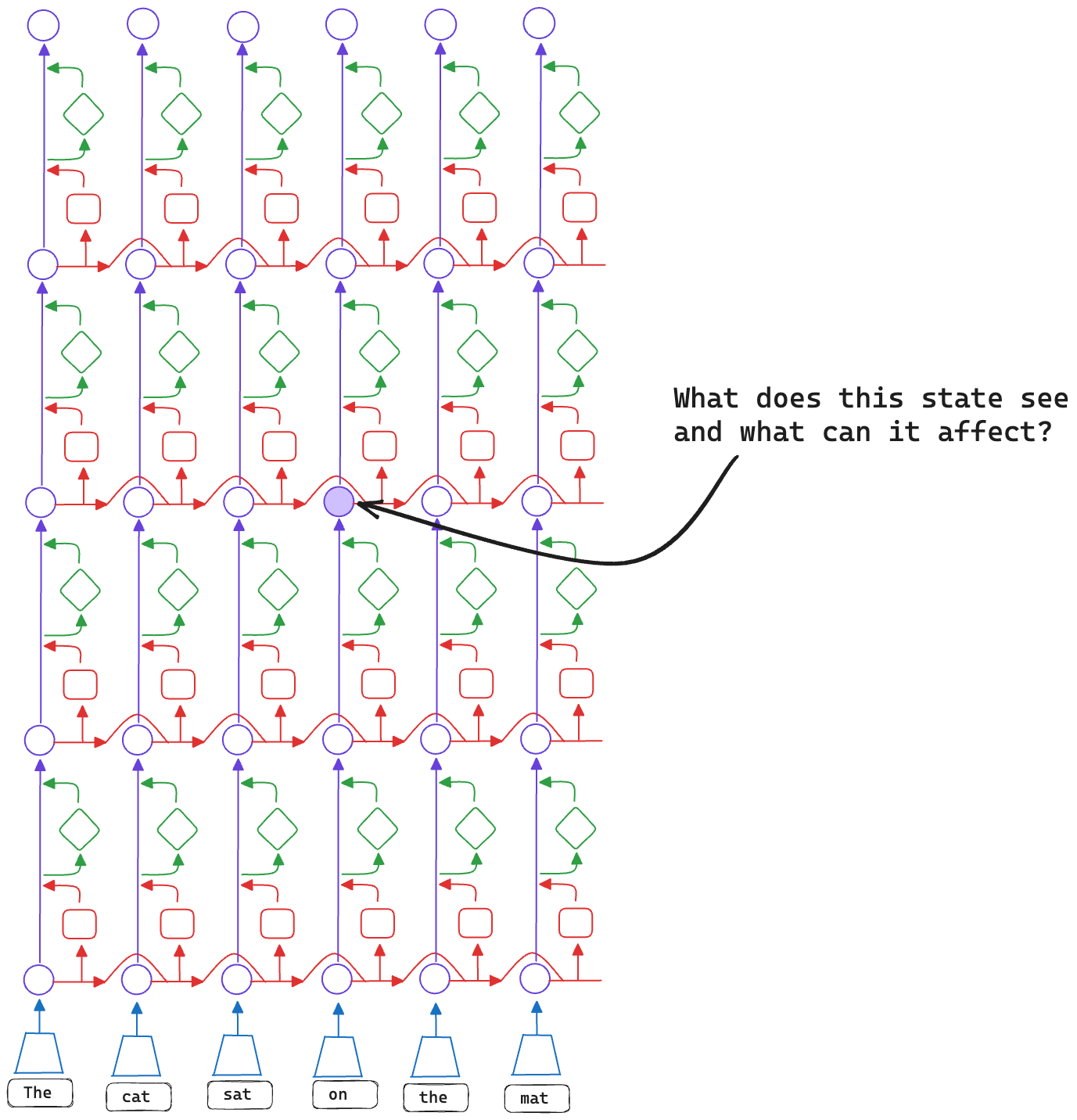
Consider the hidden state \(h_{t, n}\) (the output of the nth layer at position t). Which states can influence it? Which states can it influence?
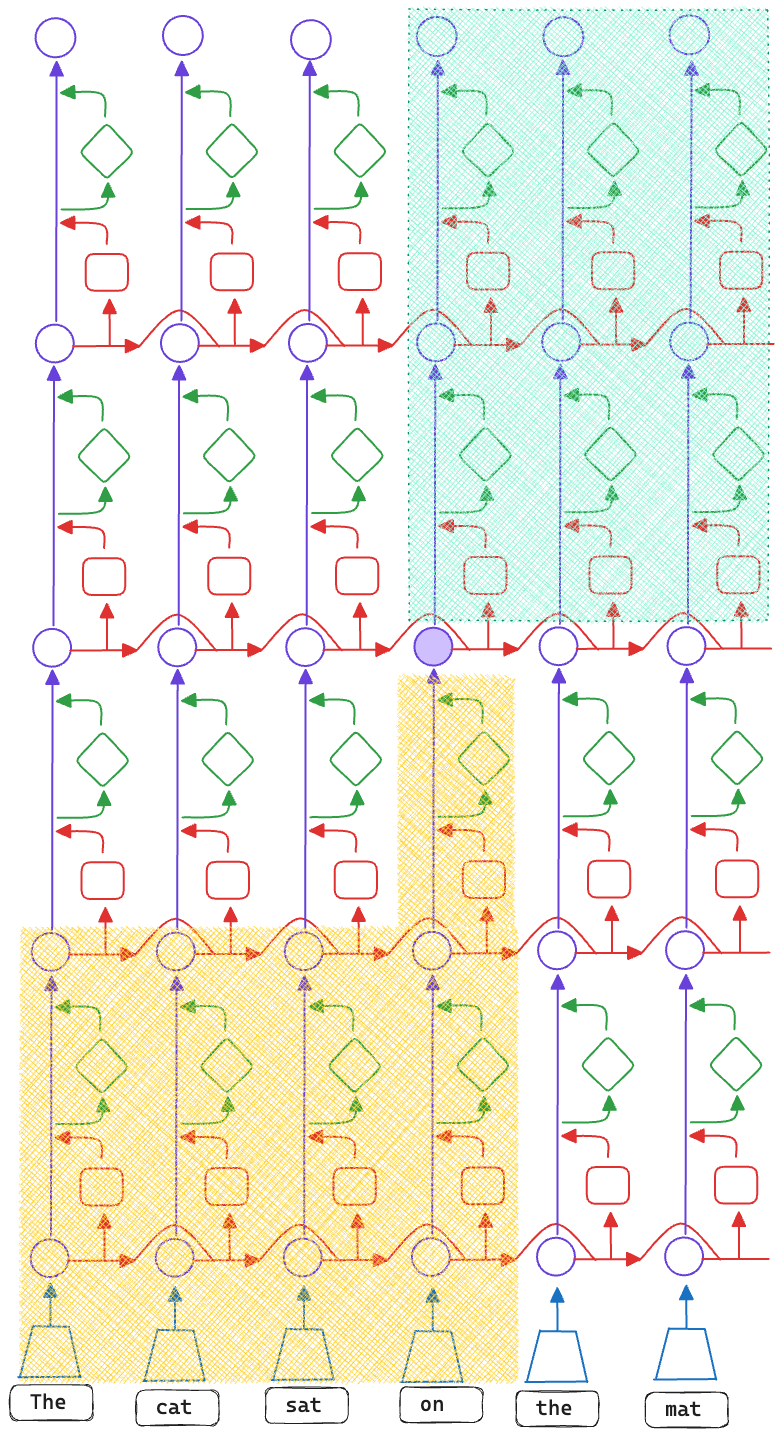
h is influenced by hidden states in the bottom left quadrant and can influence hidden states in the top right quadrant.
One way to visualise this is to compute the derivative of h with respect to preceding hidden states and the derivative of later hidden states with respect to h. We can then plot the results as a heatmap.
This is a plot of position 10, layer 5 for gpt2-small. Input text is <|endoftext|>It is done, and submitted. You can play “Survival of the Tastiest
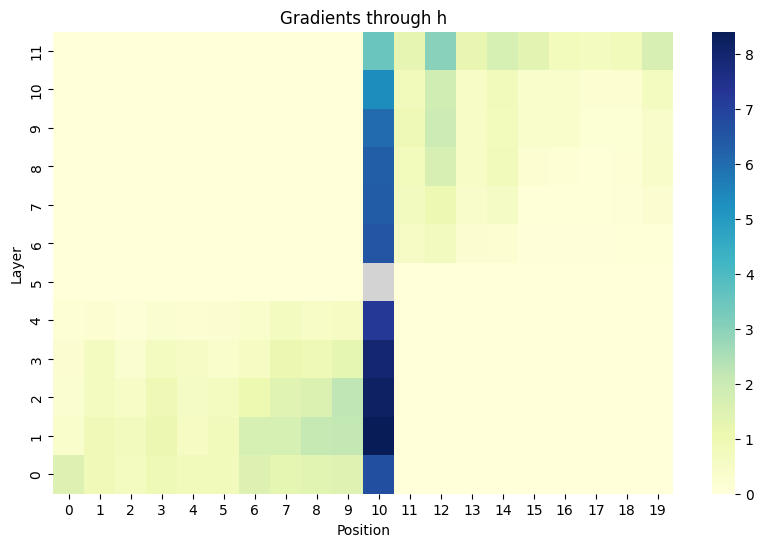
The code I used to generate this is here. Note: I haven’t yet settled on how to normalise the hidden states. I’m currently using the L2 norm of the hidden state and then summing all the gradients for each position.
We can compute the same heatmap for all positions and layers:
Hover over the points to see the heatmaps
Speculation on what this means for features
Since early layers can’t see later layers and late layers can’t influence the early layers, I’m guessing that:
- Early layers extract features that are useful at future token positions.
- Late layers try to predict the next token.